Attentive Care: How To Treat Muscle Atrophy In Cerebral Palsy Patients
Cerebral palsy is a disorder that affects the body’s muscles and motor skills. It is caused by damage to the brain, either before, during, or shortly after birth. It is one of the most common childhood disabilities, affecting approximately 8 out of every 1000 children. It can range from mild to severe and can cause a variety of physical and cognitive impairments.
One type of cerebral palsy is called hemiplegia. It affects one side of the body, making it difficult for the person to move that side. The cause of hemiplegia is usually a stroke that occurs during pregnancy or delivery. It can also be caused by birth trauma, such as a head injury or oxygen deprivation. In some cases, doctors may be held liable and sued for not recognizing or responding to signs of birth trauma that could have led to cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy can cause a variety of other medical conditions, including seizure disorders, vision and hearing problems, and muscle atrophy. It can also lead to difficulty with speech and communication as well as cognitive delays. The severity of the disability and the associated medical conditions can range from mild to severe. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential for optimizing the quality of life of those with cerebral palsy.
What Is Muscle Atrophy?
Muscle atrophy is a condition that occurs when muscles shrink and weaken due to lack of use or another underlying condition. This can be caused by a number of factors, including aging, disease, malnutrition, and certain medical conditions.
In the case of cerebral palsy, muscle atrophy can occur when muscles are not used due to limited mobility or when nerve signals are not properly sent from the brain to the muscles. This can result in weakened muscles and reduced muscle mass. It can also cause pain, fatigue, and difficulty performing everyday tasks. People with cerebral palsy who experience muscle atrophy may need to use assistive devices to help them move and complete daily activities.
Diagnosing Muscle Atrophy

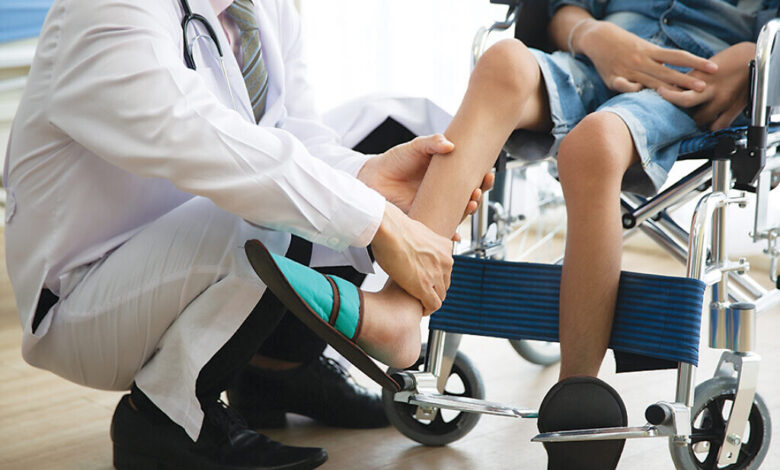
The process of diagnosing muscle atrophy begins with a physical examination by a doctor or physical therapist. During the examination, the doctor will look for signs of muscle wasting, such as reduced muscle size and strength, as well as decreased range of motion. The doctor might also order an MRI or other imaging tests to further examine the muscles.
The doctor may also perform certain strength tests to measure the strength and range of motion of the affected muscles. This can help to determine which muscles are affected by atrophy and to what degree. The doctor may also take a medical history to look for any underlying conditions that could be causing muscle wasting.
If muscle atrophy is suspected, the doctor may order a blood test to look for any underlying medical conditions. In addition, the doctor may suggest physical or occupational therapy to help the patient manage muscle wasting. Finally, the doctor may recommend lifestyle changes or medications to help improve muscle strength and function.
Treating Muscle Atrophy
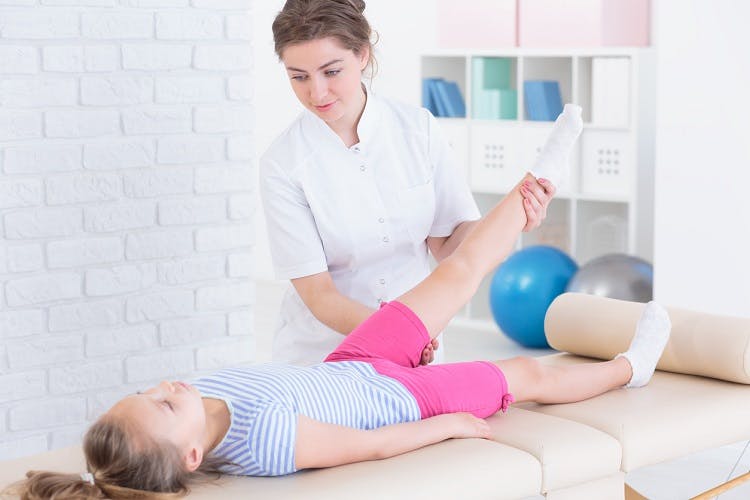

The first step in treating muscle atrophy is to identify any underlying medical conditions that may be causing it. Depending on the root cause, medications may be prescribed to help improve muscle strength and function. Physiotherapy or occupational therapy can also be beneficial in helping the patient manage muscle wasting. These therapies can help to strengthen weak muscles, improve range of motion, and restore function.Z
Range of motion exercises are an important part of physical therapy for muscle atrophy.
Passive Range of Motion Exercises: Passive range of motion exercises involve the patient performing stretching and joint movements without actively engaging the muscles. The therapist assists the patient in moving the joints, helping to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion. These exercises can be done lying down, sitting, or standing, depending on the patient’s abilities.
Active Range of Motion Exercises: Active range of motion exercises involve the patient actively engaging their muscles to move the joint. These exercises help to improve strength, coordination, and mobility. They can include exercises such as arm lifts, leg lifts, and core exercises.
Isometric Range of Motion Exercises: Isometric range of motion exercises involve the patient applying force against a stationary object, such as a wall, to engage the muscles and improve strength and range of motion. These exercises can help to improve muscle endurance and strength in the affected muscles.
Functional Range of Motion Exercises: Functional range of motion exercises involve the patient performing activities of daily living in order to improve strength, coordination, and mobility. These exercises can include activities such as climbing stairs, carrying objects, or walking. These exercises can be adapted to the patient’s abilities and can help to improve their ability to perform everyday tasks.
Strength training exercises are also beneficial for those with muscle atrophy. These exercises can help to increase muscle strength and endurance, which can help to improve the patient’s ability to perform everyday tasks. The therapist may also use resistance bands and weights to help build muscle strength.
A physical therapist may also use balance and coordination exercises to help improve mobility and prevent falls. These exercises can help to improve balance and coordination, as well as build strength in weak muscles. They may use functional exercises to help the patient perform everyday tasks. These exercises can help to improve the patient’s ability to perform tasks such as walking, dressing, and grooming. Functional exercises can also help to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Other Treatments

In addition to medical and therapeutic interventions, lifestyle changes can also help to improve muscle atrophy. Regular exercise can help to increase muscle strength and endurance and reduce the effects of muscle wasting. Eating a balanced diet with adequate amounts of protein can help to nourish the muscles and promote healthy muscle growth. Additionally, getting enough rest and avoiding excessive stress can help to reduce muscle fatigue and improve overall muscle health.
For those with cerebral palsy, assistive devices such as wheelchairs or walkers can help to improve mobility and reduce strain on weakened muscles. Adaptive exercises and other activities can also be beneficial in helping to improve muscle strength and function. Finally, supportive counseling can help the individual cope with the emotional and social aspects of living with a disability.
Treating muscle atrophy is important for those with cerebral palsy, as it can improve mobility, strength, and range of motion.