Green and Lean: The Plant-Based Path to Weight Management
In recent years, the shift towards more sustainable and health-conscious eating patterns has led many to explore the world of plant-based diets. These diets, which emphasize fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes while minimizing or eliminating animal products, are not just a fleeting trend but are backed by a growing body of scientific evidence. Research suggests that adopting a plant-based dietary approach can offer a plethora of health benefits, including improved weight management.
As obesity and related health complications continue to rise, understanding the connection between plant-based eating and weight management has never been more critical. This article explores the idea of plant-based diets, elucidating their types, nutritional profiles, and their profound impact on weight and overall health. Whether you’re curious about the basics or considering a dietary transition, we’ve got the information you need to understand the green world of plant-based nutrition.
Nutritional Basics of Plant-Based Diets
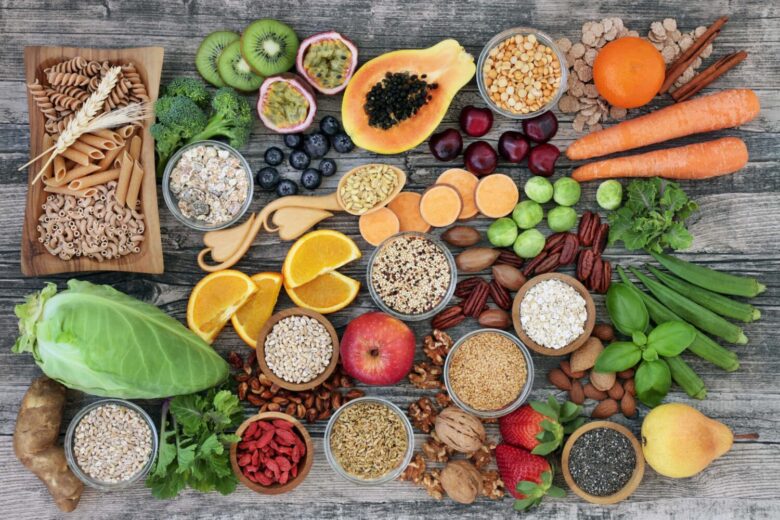

At the core of plant-based diets are nutrient-dense foods that are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. When properly planned, these diets can provide all the essential macronutrients – proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. For instance, while meat is often cited as a primary protein source, many plant-based alternatives like lentils, beans, quinoa, tofu, and tempeh offer robust protein profiles. Healthy fats can be sourced from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, while whole grains, vegetables, and fruits serve as primary carbohydrate sources. The emphasis on whole foods means that individuals on plant-based diets often consume fewer processed foods, reducing their intake of added sugars, salts, and unhealthy fats.
Beyond the macronutrients, plant-based diets are abundant in essential micronutrients. For example, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds are rich in magnesium and iron; fruits like oranges and strawberries provide ample vitamin C; and flaxseeds and chia seeds are excellent sources of Omega-3 fatty acids. However, those on strict vegan diets might need to be mindful of certain nutrients like Vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products, and may require supplementation or fortified foods. As with any diet, variety is key. By consulting with a weight loss Atlanta nutritionist, one can ensure a balanced intake of essential nutrients, fostering not only weight management, but also overall health and vitality.
How Plant-Based Diets Aid in Weight Management
One of the primary ways plant-based diets contribute to weight management is through natural caloric reduction. Foods predominant in plant-based diets, such as vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains, are inherently high in fiber and water content. This combination not only increases feelings of fullness and satiety but also does so with fewer calories compared to many animal-based and processed foods. The result is a spontaneous reduction in calorie intake without the necessity of rigorous calorie counting or restrictive portioning. The fiber-rich nature of these foods also plays a pivotal role in improving gut health. Dietary fiber acts as a prebiotic, fostering a healthy gut microbiota. A balanced gut flora has been linked to improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and even better metabolic health, all of which can further support weight management endeavors.
Plant-based diets have shown significant promise in reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Regular consumption of plant-based foods has been associated with lowered risks of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. For instance, the antioxidants and phytochemicals found in plants help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, two key factors in many chronic diseases. Plant-based diets often lead to improved lipid profiles, with reductions in LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, both of which are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
Practical Tips for Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
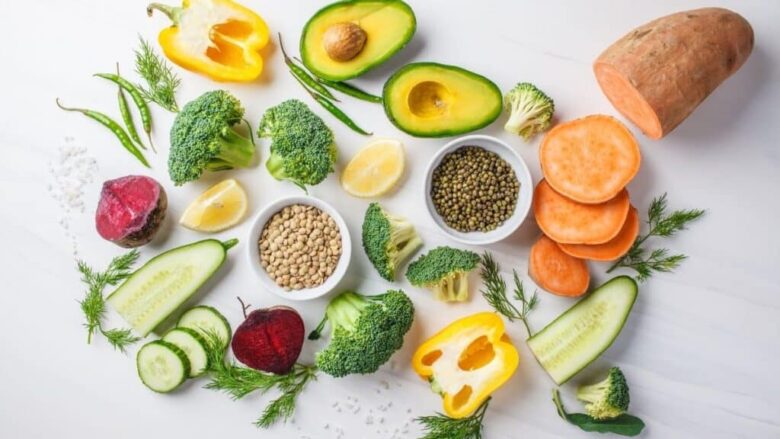

Moving towards a plant-based diet for weight management doesn’t necessitate an abrupt overhaul of one’s eating habits overnight. A gradual approach often proves most effective, allowing individuals to adapt and refine their choices over time. A good starting point is to incorporate one plant-based meal a day, allowing the transition to be more manageable and less daunting. Over time, as one becomes accustomed to new flavors, textures, and meal patterns, it becomes easier to expand this to multiple meals and snacks. Another practical strategy is meal planning. By setting aside some time each week to plan meals, one can ensure a balanced intake of nutrients, avoid repetitive menus, and reduce the likelihood of resorting to less nutritious, convenience-driven options. Investing in a few plant-based cookbooks or following reputable plant-based blogs can offer a wealth of meal ideas and recipes.
To prevent nutritional gaps and keep meals exciting, it’s important to consume a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This not only ensures a broad spectrum of nutrients but also introduces the palate to an array of flavors and cuisines. Mindful eating and portion control remain . While plant-based foods are generally lower in calories, it’s still possible to overeat. By listening to one’s body, recognizing satiety cues, and adjusting portion sizes accordingly, individuals can maximize the weight management benefits of a plant-based diet without feeling deprived or restricted.
Plant-based diets offer a holistic approach to weight management, emphasizing nutrient-rich foods that promote satiety, gut health, and overall wellness. As research continues to underscore the myriad benefits of such dietary patterns, it’s evident that moving towards a plant-centric way of eating can be a viable and sustainable strategy for many. With thoughtful planning and an open mind to new culinary experiences, transitioning to a plant-based diet can pave the way for many improved health outcomes.